Wide bandgap components for power conversion
What are the advantages of integrating SiC and GaN components into power architectures ?

A growing power consumption
The development of power sources and consumers requires better performance from power converters. Innovative components as Gallium Nitride (GaN), coming from wide bandgap semiconductors, emerge as solutions to this increased performance need.
Power consumption continues to increase because of the development of:
- Electric means of transportation
- Solar panels or wind turbine farms
- Digital tools and data centers
- Electric equipment and machinery
The efficiency of electric systems has become a major issue, considering the equilibrium between:
- Performance (mostly power yield and density)
- Costs
The consideration of these criteria necessarily represents a constraint on the design of the DC/DC converter architecture the choice of power components (active or passive).
Evolution of the technology of components
In order to improve performance, research has been conducted on materials and technologies used for power components.
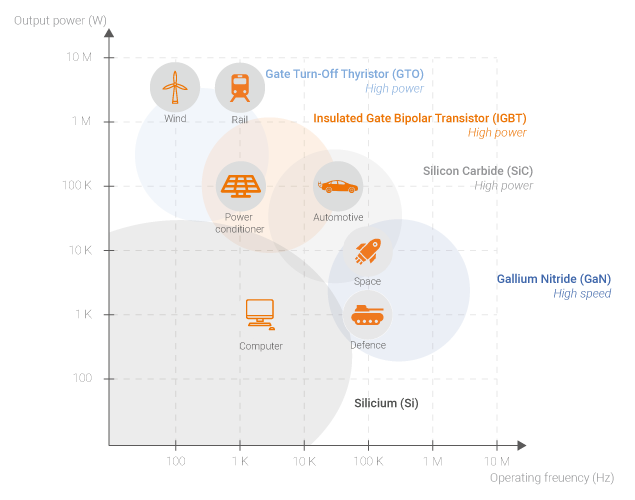
Wide bandgap semiconductors, such as Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Gallium Nitride (GaN), allow for the development of power transistors capable of outperforming current MOSFET or IGBT standards. In fact, wide bandgap semiconductors make it possible:
- To significantly reduce the siez of DC/DC converters
- To reach high conversion performance (yield)
The ability of wide bandgap components to commute much faster, more often and at a higher frequency than previous technologies allows for a drastic increase in the power density of power converters. This is due to both the reduction in the size of the magnetics and the simplification of the cooling system.
DCDC conversion principles
DC/DC power conversion is considered as the second floor of power conversion:
- 1st floor - AC/DC conversion
Power factor correction, non-isolated. - 2nd floor - DC/DC conversion
Voltage and output power adaptation to the application.
Possible isolation between input and output. - 3rd floor (optional) - DC bus
Smoothing of withdrawn power.
DC/DC power conversion has the function of adaptating voltage and output power to the electric load. Isolation can be necessary in some applications so as to ensure user safety.
The use of SiC and GaN components in the architectures of the DC/DC converters makes it possible to develop high-performance, innovative conversion systems.
Perspectives
Due to the yield and power density that are possible with wide bandgap semiconductors, this type of semiconductor tends to be favored in the design and manufacture of power architectures.
Emerging applications such as electric vehicles and chargers encourage the use of SiC and GaN components: bi-directional power in chargers is required to ensure the future role of electric vehicles in grid regulation. This regulation is achieved by injecting the energy stored in the charger into the grid, while at the same time maintaining the ability to transfer charge to the electric vehicle.
This application example places more stringent requirements on the power architecture and involves the use of Sic and GaN for higher performance from more compact power systems.

